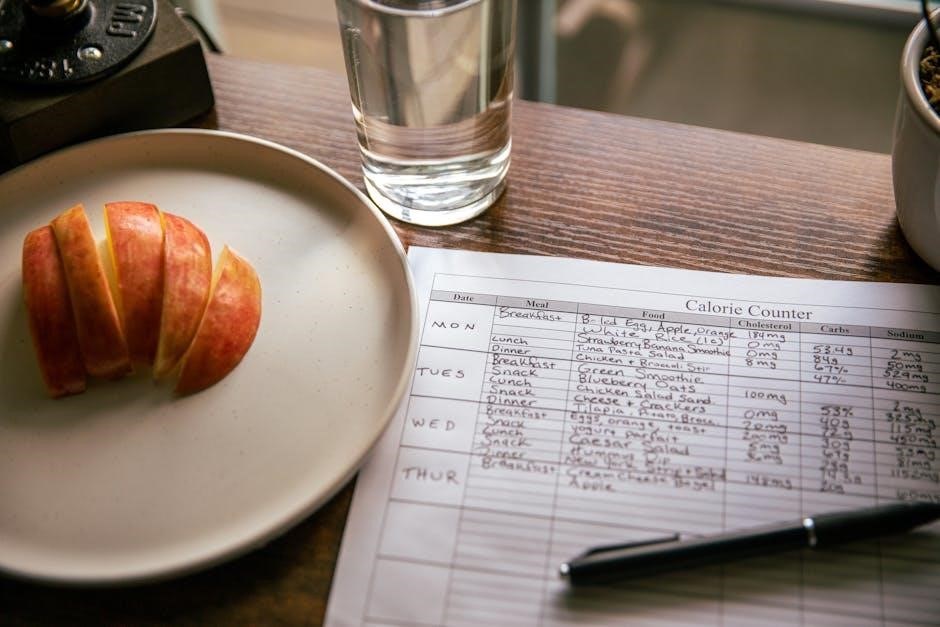
Carb cycling is a dietary strategy alternating carbohydrate intake to optimize fitness goals. A printable 12-week carb cycling meal plan PDF offers structured guidance for fat loss and performance.
What is Carb Cycling?
Carb cycling is a dietary approach that involves alternating carbohydrate intake on different days to achieve specific fitness and health goals. It typically includes low-carb days (10-20% of daily calories from carbs), medium-carb days (20-35%), and high-carb days (35% or more). This strategy manipulates carbohydrate consumption to optimize energy levels, metabolism, and fat loss while maintaining muscle mass. A printable 12-week carb cycling meal plan PDF provides a structured guide, outlining daily meals and macronutrient balances. It allows customization for individual needs, such as vegetarian or vegan preferences, and offers practical tools like recipes and shopping lists. By cycling carbs, users can avoid plateaus and support their bodies during intense training or weight loss journeys. This method is popular among athletes and dieters seeking a flexible, results-driven nutrition plan.
Benefits of Carb Cycling

Carb cycling offers numerous benefits, particularly when following a structured 12-week meal plan. It enhances fat loss by optimizing metabolic function and preventing plateaus. By alternating carbohydrate intake, individuals can maintain muscle mass while shedding unwanted fat. A printable PDF plan ensures consistency and adherence, making it easier to stick to the program. Carb cycling also improves insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Additionally, it provides mental clarity and sustained energy levels, as the body adapts to using fats and carbs efficiently. The flexibility of the plan allows for customization, catering to diverse dietary needs and preferences. Overall, carb cycling is an effective strategy for achieving weight management and improved overall health, supported by a well-organized meal plan.
How Carb Cycling Works
Carb cycling involves alternating carbohydrate intake to optimize fat loss and muscle maintenance. It works by manipulating glycogen stores, as high-carb days replenish energy reserves, while low-carb days promote fat burning. The body adapts by becoming more efficient at using both carbs and fats for fuel, preventing metabolic plateaus. A printable 12-week plan guides this process, structuring high, medium, and low-carb phases. Timing carbs around workouts enhances performance, while aligning intake with daily activities boosts efficiency. This cyclical approach keeps metabolism active and prevents over-reliance on a single fuel source. The structured plan ensures consistency, making it easier to follow and sustain long-term. By cycling carbs strategically, individuals can achieve their fitness goals effectively.

Understanding the 12-Week Carb Cycling Meal Plan
This structured plan guides users through 12 weeks of carb cycling, with clear phases and adjustments to maximize fat loss and muscle retention.
Structure of the 12-Week Plan
The 12-week carb cycling meal plan is divided into phases, starting with lower-carb weeks to promote fat loss, followed by periods of higher carbs to replenish energy and support muscle growth. Weeks 1-4 focus on adaptation, with moderate carb intake. Weeks 5-8 introduce alternating low- and high-carb days to optimize results. Weeks 9-12 emphasize maintenance, balancing fat loss and muscle retention. Each week includes detailed meal timing, portion sizes, and macronutrient ratios. Adjustments are made based on progress, ensuring the plan remains effective. The structure allows for flexibility, catering to individual goals like weight loss or muscle gain, while providing a clear roadmap for success. Regular tracking ensures the plan stays aligned with personal objectives.
Phases of Carb Cycling
The 12-week carb cycling plan is organized into distinct phases designed to maximize fat loss and muscle preservation. The first phase (weeks 1-4) focuses on adapting to lower carb intake, with an emphasis on whole foods and calorie control. Phase two (weeks 5-8) introduces alternating low- and high-carb days to boost metabolism and energy levels. The final phase (weeks 9-12) balances carb intake to maintain progress while preventing plateaus. Each phase adjusts macronutrient ratios to align with your goals, ensuring sustained results. Regular monitoring of progress helps tailor the plan to individual needs, making it adaptable and effective for long-term success. This structured approach ensures a balanced and sustainable journey toward your fitness objectives.
Importance of Meal Planning
Meal planning is essential for the success of a 12-week carb cycling program. It ensures adherence to the diet, providing structure and clarity for daily nutrition. By organizing meals in advance, individuals can avoid unhealthy choices and stay on track with their goals. A well-planned meal schedule also optimizes performance and recovery, as it aligns with training and rest days. Additionally, meal planning helps manage portion sizes and macronutrient balances, preventing overeating or nutrient deficiencies. For those with dietary restrictions, such as vegetarians or vegans, meal planning is crucial for ensuring variety and meeting nutritional needs. Consistency is key, and a planned approach makes maintaining the carb cycling regimen sustainable and stress-free.

Macronutrient Breakdown
A balanced mix of carbohydrates, protein, and fats is crucial for energy, muscle repair, and overall health in a carb cycling plan.
Carbohydrates: Types and Sources
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source and play a vital role in carb cycling. They are categorized into simple (sugars) and complex (starches, fibers) carbs. Whole, unprocessed foods like whole grains, vegetables, and legumes are ideal sources, providing sustained energy and essential nutrients. For a 12-week plan, focusing on low-glycemic carbs such as oats, quinoa, and sweet potatoes helps regulate blood sugar levels. Avoiding refined sugars and processed carbs ensures better metabolic control. Incorporating a variety of colorful vegetables adds fiber, which supports digestion and satiety. Balancing carb intake with protein and fats maintains overall nutritional harmony, making it easier to stick to the meal plan and achieve weight management goals.
Protein: Role and Requirements
Protein is essential for muscle repair, growth, and overall health, making it a cornerstone of a carb cycling meal plan; It helps maintain muscle mass during calorie restriction and supports metabolism; The recommended daily intake varies based on weight, activity level, and goals, typically ranging from 1.2 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight. High-quality sources include lean meats (chicken, turkey), fish (salmon, tuna), eggs, dairy, and plant-based options like legumes and tofu. Adequate protein intake ensures satiety and prevents muscle breakdown, especially during low-carb phases. Balancing protein with carbs and fats optimizes energy levels and supports fat loss. Incorporating a variety of protein sources ensures a well-rounded diet tailored to individual needs and preferences.
Fats: Healthy Sources and Importance

Fats are a vital component of a balanced diet, providing energy, aiding in hormone production, and supporting the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish (e.g., salmon and mackerel). These fats improve heart health and reduce inflammation. Saturated fats, while beneficial in moderation, should be consumed mindfully. Trans fats, often in processed foods, should be avoided. Incorporating a variety of healthy fats into your carb cycling meal plan enhances satiety, supports metabolic function, and ensures overall nutritional balance. They play a key role in managing hunger and energy levels, especially during low-carb phases. Balancing fat intake with protein and carbs is essential for optimal results.

Meal Timing and Frequency
Proper meal timing and frequency optimize metabolism, regulate blood sugar, and maintain energy levels. A structured schedule balances macronutrient intake, supporting fat loss and muscle maintenance goals effectively. Consistency is key.
Optimal Meal Times
Optimal meal timing is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of a carb cycling plan. Eating within an hour of waking up helps kickstart metabolism, while spacing meals every 3-4 hours maintains energy levels and supports fat loss. For carb cycling, aligning meals with workout schedules is key—consume carbs and protein post-exercise to aid recovery and muscle growth. Timing high-carb meals earlier in the day ensures better utilization, while low-carb meals can be reserved for rest days. Consistency is vital, as irregular eating patterns can disrupt metabolic rhythms. Adjust meal times based on personal schedules, but aim to maintain a balanced intake throughout the day. This approach supports both weight management and overall health.
Intermittent Fasting and Carb Cycling
Intermittent fasting can complement a carb cycling plan by enhancing fat loss and improving insulin sensitivity. By restricting eating to a specific window, such as 8 hours, you align your meals with your energy needs. On low-carb days, fasting can amplify fat burning, while on high-carb days, it ensures efficient nutrient utilization. This combination helps maintain metabolic flexibility, allowing your body to switch between using carbs and fat for fuel. To integrate intermittent fasting with carb cycling, start with a 16:8 fasting schedule and adjust based on tolerance. Pairing fasting with carb cycling can boost results, but listen to your body and adapt as needed to avoid burnout or nutrient deficiencies. This dual approach supports both weight loss and overall metabolic health.
Snacking Strategies
Snacking plays a crucial role in maintaining energy levels and metabolism throughout the day. When following a carb cycling meal plan, snacks should align with your daily carb intake. On low-carb days, opt for protein-rich snacks like hard-boiled eggs, Greek yogurt, or a handful of nuts. For medium and high-carb days, include complex carbs such as fruits, veggie sticks with hummus, or whole-grain crackers. Portion control is essential to avoid overeating, especially on high-carb days. Staying hydrated is also key, as thirst is often mistaken for hunger. Aim to snack mindfully, choosing nutrient-dense options that support your goals. Avoid sugary or processed snacks, as they can disrupt your progress. Regular, balanced snacks help maintain focus and prevent cravings.

Customizing the Meal Plan
Tailor your 12-week carb cycling plan to fit personal preferences, dietary needs, and lifestyle. Adjust portion sizes, swap ingredients, and incorporate vegetarian, vegan, or gluten-free options as needed.
Adjusting for Caloric Needs
Caloric intake plays a crucial role in achieving your goals with carb cycling. Start by calculating your maintenance calories based on weight, activity level, and goals. For weight loss, create a caloric deficit by reducing daily intake by 500-750 calories. For muscle gain, aim for a surplus of 250-500 calories. Adjust portion sizes across meals, focusing on protein and healthy fats to maintain satiety. Increase or decrease carbohydrate intake on high-carb days to align with energy needs. For example, active individuals may require more carbs for fuel, while sedentary individuals might need fewer. Track progress weekly and tweak caloric intake to ensure steady results. Balancing macronutrients while adjusting calories is key to sustaining momentum and achieving desired outcomes.
Vegetarian and Vegan Options
A well-structured 12-week carb cycling meal plan can easily accommodate vegetarian and vegan diets by focusing on plant-based protein and carbohydrate sources. Incorporate legumes, beans, lentils, and tofu for protein, and whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats for carbs. Vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, and sweet potatoes provide essential nutrients and fiber. For vegans, ensure adequate intake of vitamin B12 and omega-3s through fortified foods or supplements. Plant-based milks and nut butters are great for adding healthy fats. Meal prepping can help maintain variety and ensure nutritional balance. By carefully selecting whole, minimally processed foods, vegetarians and vegans can thrive on a carb cycling plan while supporting their health and fitness goals. This approach promotes sustainability and aligns with ethical dietary preferences.
Dietary Restrictions and Preferences
A printable 12-week carb cycling meal plan can be tailored to accommodate various dietary restrictions and preferences, ensuring inclusivity for all users. For those with gluten intolerance, gluten-free alternatives like cauliflower rice, zucchini noodles, and gluten-free grains can be incorporated. Dairy-free options such as almond milk, coconut yogurt, and vegan cheeses are suitable for lactose intolerant individuals. Soy-free and low-FODMAP diets can also be supported by substituting ingredients like tofu with grilled meats or vegetables. Additionally, halal, kosher, and keto-friendly options can be integrated by using certified meats and low-carb, high-fat substitutes. By carefully selecting ingredients and reading labels, individuals with specific dietary needs can thrive while following the carb cycling plan; This flexibility ensures the meal plan is adaptable to diverse lifestyles and preferences, promoting long-term adherence and success.

Sample Meal Plan Overview
A printable 12-week carb cycling meal plan provides structured guidance, balancing macronutrients and calorie intake across low, medium, and high-carb phases for optimal results and variety.
Low-Carb Day Example
A low-carb day focuses on restricting carbohydrate intake to deplete glycogen stores, promoting fat loss. A sample meal plan includes scrambled eggs with spinach and avocado for breakfast, a snack of Greek yogurt with almonds, grilled chicken salad with olive oil dressing for lunch, and baked salmon with cauliflower rice and green beans for dinner. Macronutrient breakdowns emphasize high protein and healthy fats, with minimal carbs from vegetables. Beverages like water and herbal teas are encouraged. This structure helps maintain energy levels while adhering to carb cycling principles. Portion control and food quality are critical to achieving desired results.
Medium-Carb Day Example
A medium-carb day balances carbohydrate intake to replenish energy stores while maintaining fat loss progress. A sample meal plan includes oatmeal with berries and nuts for breakfast, a snack of apple slices with peanut butter, grilled chicken with quinoa and steamed vegetables for lunch, and salmon with sweet potato and asparagus for dinner. This day focuses on complex carbs like whole grains and starchy vegetables, paired with lean proteins and healthy fats. Portion sizes are adjusted to meet caloric needs, ensuring a balanced macronutrient intake. This structure supports muscle recovery and sustained energy levels, aligning with the carb cycling goals of fat loss and muscle maintenance.
High-Carb Day Example
A high-carb day focuses on replenishing glycogen stores and boosting metabolism, typically after low-carb days. Breakfast might include whole-grain pancakes with fresh fruit and a scoop of whey protein. A mid-morning snack could be Greek yogurt with honey and mixed berries. Lunch could feature brown rice with grilled chicken, roasted vegetables, and a side of quinoa. An afternoon snack might include a smoothie with oats, banana, and almond milk. Dinner could consist of sweet potato mash, lean beef stir-fry with broccoli, and a small portion of whole-grain bread. This day emphasizes complex carbs, lean proteins, and healthy fats to support energy and muscle recovery. Portion sizes are adjusted to meet individual caloric needs, ensuring progress toward fat loss and muscle maintenance goals.

Shopping and Meal Prep
Plan your meals weekly, create a grocery list, and prep ingredients in advance. Use containers for portion control and schedule prep sessions to stay organized and consistent.
Creating a Grocery List
A well-organized grocery list is essential for a 12-week carb cycling meal plan. Start by categorizing items like proteins, carbs, and fats. Include lean meats, fish, eggs, and plant-based proteins for protein sources. For carbohydrates, list whole grains, vegetables, and low-sugar fruits. Healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and seeds should also be included. Don’t forget snacks and condiments to keep meals flavorful. Prioritize fresh ingredients for optimal nutrition and adjust quantities based on your caloric needs. Planning your list weekly ensures freshness and reduces waste. Use the printable PDF as a guide to avoid missing any essentials. This structured approach helps maintain consistency and keeps your diet on track throughout the 12-week cycle.
Meal Prep Tips for Success
Meal prepping is a cornerstone of a successful 12-week carb cycling plan. Start by designating a specific day for meal preparation, such as Sunday, to ensure consistency. Use airtight containers to store meals, keeping them fresh for up to 3-4 days. Batch cooking proteins, veggies, and grains saves time and reduces food waste. Label and date all containers for easy tracking. Incorporate variety to avoid meal fatigue, alternating flavors and ingredients. Pre-cut vegetables and portion out snacks to streamline daily meals. Consider freezing meals for later weeks to maintain convenience. Staying organized and consistent with meal prep ensures adherence to the plan and supports long-term success.
Staying Organized
Staying organized is key to successfully following a 12-week carb cycling meal plan. Begin by using a planner or digital app to schedule meals, workouts, and grocery trips. Create a master grocery list based on your weekly meal plan to avoid last-minute decisions. Store meals in labeled, dated containers for easy identification. Keep track of progress by maintaining a journal to monitor weight, measurements, and how you feel. Regularly review and adjust your plan to ensure alignment with your goals. An organized approach minimizes stress and maximizes adherence, helping you stay on track throughout the 12-week journey. Consistency and planning are essential for achieving optimal results.

Tracking Progress
Tracking progress weekly helps monitor weight, body fat, and measurements. Use a journal to log workouts, meals, and health markers. Progress photos and adjustments ensure motivation and success.
Monitoring Weight and Measurements
Monitoring weight and measurements is crucial for tracking progress in a carb cycling plan. Weigh yourself weekly, preferably on the same day and time, to observe trends. Use a tape measure to track changes in body circumference, such as waist, hips, and thighs. These metrics provide insight into fat loss and muscle retention. Documenting progress helps identify patterns and ensures accountability. Regular measurements also help adjust caloric intake and macronutrient ratios as needed. While weight fluctuations can occur, consistent tracking over time offers a clear picture of overall progress. This data is essential for fine-tuning the meal plan to achieve desired results.
Adjusting the Plan as Needed
Regularly reassessing and adjusting your carb cycling plan ensures continued progress toward your goals. If weight loss stalls or muscle gain plateaus, it may be necessary to tweak caloric intake, macronutrient ratios, or the intensity of workouts. Pay attention to how your body responds to high-carb, medium-carb, and low-carb days. Adjustments might include increasing or decreasing carb intake, altering protein portions, or modifying meal timing. Stay flexible and patient, as progress can vary. Tracking weight, measurements, and energy levels helps identify when changes are needed. Small modifications, such as swapping food choices or adjusting portion sizes, can reignite progress. Consistent monitoring ensures the plan remains effective and tailored to your evolving needs. Trust the process and stay committed to achieve optimal results.
Maintaining Motivation
Staying motivated throughout a 12-week carb cycling plan requires consistent effort and mindset shifts. Setting clear, achievable goals helps maintain focus and drive. Celebrate small victories, like completing a week or noticing energy improvements, to build confidence. Surround yourself with supportive friends or join a community for accountability. Tracking progress visually, such as through photos or a journal, can reinforce commitment. Remind yourself why you started, whether for better health, improved physique, or increased energy. Stay positive and embrace the journey, even when challenges arise. Reward yourself with non-food treats to stay motivated without derailing your progress. Consistency is key, so keep your eyes on the prize and celebrate every step forward.